
The demand for stainless steel continues to grow across industries due to its combination of corrosion resistance, versatility, and strength. Still, prices can fluctuate depending on the grade, raw material costs, and geopolitical conditions. This guide will explore the key elements influencing stainless steel prices, breakdowns of different grades, and cost management strategies.
So what is the price of stainless steel?
The price of stainless steel is normally in the range of the following table:
| Grade | Typical Use | Average Cost Per Ton (USD) |
| 304 | Kitchenware Food Processing | $2,500 – $3,200 |
| 316 | Marine Parts Medical Devices | $3,500 – $4,000 |
| 430 | Household Appliances | $1,800 – $2,300 |
Introduction to Stainless Pricing
Stainless steel is essential in the automotive, construction, household, and medical industries. Its corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and durability make it highly desirable, but these qualities contribute to the variable pricing.
From skyscrapers to medical instruments, stainless steel is the cornerstone material that many sectors rely on for longevity and safety. In 2024, stainless steel prices were influenced by several factors, including the type of steel, chain dynamics, global supply, and raw material cost.
In addition to the prices, recent global economic fluctuations, pandemic-related supply chain constraints, and trade policy shifts have created volatility in stainless steel pricing.
A comprehensive understanding of these drivers will help you to make an informed purchasing decision and manage costs effectively.
Key Factors Affecting Stainless Steel Pricing
- Global Demand: As the world economy recovers and industries ramp up, demand surges and prices increase.
- Raw Material Volatility: Chromium, nickel, and molybdenum are the core components of stainless steel, and price shifts in these materials can impact the cost.
- Environmental Policies: With stricter emission controls, especially in the significant steel-production countries, you see increased production costs.
The Price Differences Between Different Stainless Steel Types
The type or grade used significantly affects costs when determining stainless steel prices. Each type has a unique composition and properties tailored to meet the specific demands of various industries.
| Grade | Main Elements | Properties | Common Applications |
| 304 (18/8) | 18% Chromium 8% Nickel | Versatile Formable Good Corrosion | Kitchenware Appliances Architectural Panels |
| 316 (16/10) | 16% Chromium 10% Nickel | Excellent Corrosion Excellent For High Temperatures | Marine Applications Chemical Processing Equipment |
| 430 | 16% Chromium | Magnetic Lower Corrosion | Automotive Trim Appliances |
304 Stainless Steel

This steel is known for its corrosion resistance and versatility. It is widely used in food processing, industrial environments, and kitchenware. The high chromium and nickel content makes it more costly.
However, it is essential for applications where durability and resistance to everyday use are needed. With its popularity, you will find it widely available, keeping price fluctuations in check.
316 Stainless Steel

Adding molybdenum to stainless steel enhances corrosion resistance, especially in chemical and saltwater environments. The 316-grade application is preferred in medical devices and marine parts, justifying a higher cost than the 304-grade stainless steel. In 2024, the demand for this steel was higher in the medical field, where stringent standards make this grade indispensable.
430 Stainless Steel
The 430-grade stainless steel is a lower-cost option as it lacks nickel. It is also used in household appliances and decorative applications. While it lacks some corrosion resistance, it remains affordable and attractive if you have budget-conscious applications with minimal exposure to harsh environments.
Price Variations by Stainless Steel Grade
Each grade has a unique property that drives cost and suitability across industries. For example, 316-grade stainless steel has superior corrosion resistance. It commands a premium price in sectors like marine applications and pharmaceuticals, where durability is essential.
Factors That Influence Stainless Steel Prices
When it comes to the question of what stainless steel price is, different factors can affect the cost.
Raw Material Costs
The main components of stainless steel are chromium, iron, nickel, and sometimes molybdenum.
Nickel significantly impacts the pricing due to its high cost and use across various steel grades.
Mining output, geopolitical stability in source countries, and demand from other industries, such as the manufacturing of batteries for electric vehicles, can affect prices for these metals.
Supply And Demand
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and construction are the main drivers of demand for stainless steel.
As these sectors expand or contract, so does the need for steel, creating price shifts in response to how the market changes.
A construction boom, for instance, increases the demand for 304 steel for its versatility and strength.
Manufacturing Process
The production process of stainless steel is complex, including melting, casting, and finishing, each of which adds to the final cost. High-quality finishes and heat treatments add to the processing costs to meet the industry standards compared to other metals.
Geopolitical Factors
Other costs affecting the price of stainless steel are tariffs, trade restrictions, and import/export policies.
Trade tensions between major economic countries can restrict raw material availability, leading to higher prices and the supply chain.
The same goes for environmental regulations in the central producing countries, which lead to higher production costs as manufacturers implement emission-reduction technologies.
Stainless Steel Market Trends
In 2024, stainless steel prices followed several trends influenced by economic recovery and sector-specific growth.
Historical Trends
Historically, stainless steel prices have risen, as seen in the chart, due to the increasing demand for and cost of raw materials.
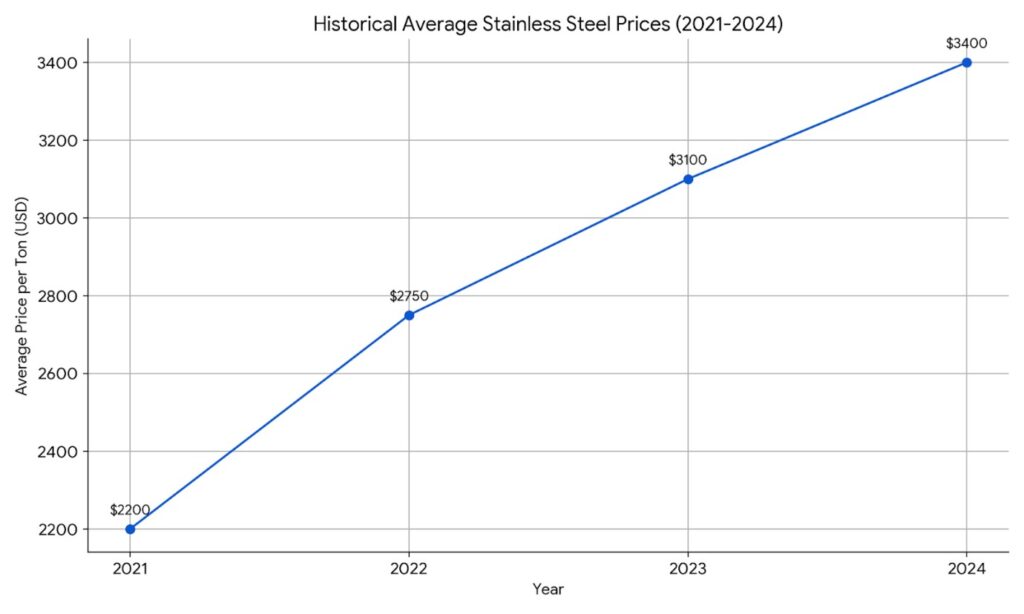
As industries like renewable energy and electric vehicle manufacturing expand, the demand for stainless steel grows, leading to upward pressure on prices.
Seasonal Impacts
Seasonal demand also plays a part in the cost of stainless steel, especially in the automotive and construction sectors. For instance, demand will peak during the warmer months when construction projects start again. Planning your purchases allows you to take advantage of seasonal price dips and avoid paying higher costs.
Comparing Stainless Steel With Alternative Materials
When choosing materials, it helps to compare stainless steel to alternatives like carbon steel, plastics, and aluminum. Each material has unique properties that can impact the cost when used in various applications.
| Material | Cost Per Ton (USD) | Durability | Typical Applications |
| Stainless Steel | $2,500 – $3,600 | High | Construction Medical Kitchenware |
| Carbon Steel | $1,200 – $1,800 | Moderate | Construction Machinery |
| Aluminum | $1,800 – $2,500 | Moderate | Aerospace Transport |
| Plastics | $500 – $1,500 | Low | Packaging Disposable Items |
Carbon Steel: The metal is often cheaper but lacks corrosion resistance. It is suitable for indoor applications or in environments without concern for rust. The metals used in machinery and construction where strength plays an important role. Still, there is minimal exposure to moisture.
Aluminum: It is a lightweight material with corrosion resistance but lacks the durability of stainless steel. It is used in aerospace industries where weight is essential. While it is less durable, it performs well in packaging and transport applications.
Plastics: The material is inexpensive and lightweight but not as durable. Plastics serve well in disposable applications or for products that do not require a high strength. Yet, stainless steel remains superior in an environment where resistance to wear and longevity counts.
Estimated Cost As Per Application
The cost of stainless steel can vary depending on the intended application.
Industrial Use
For large-scale applications, stainless steel typically costs around $2,500 to $3,600 per ton. Bulk orders may qualify for discounts, lowering the per-ton cost. Industrial projects benefit from stainless steel’s resilience in harsh environments, making it a cost-effective investment in the long run.
Commercial and Household Products
Products such as kitchenware and appliances have higher per-kilogram costs due to additional processing requirements, like polishing and finishing. Depending on the grade, a kitchen remodel using stainless steel fixtures can range between $500 and $1,500.
Project Examples
In the medical sector, where precision and safety are crucial, costs rise with higher-grade stainless steel like 316. This grade is critical for equipment that must withstand sterilization and resist corrosion.
8 Tips For Buyers to Manage Stainless Steel Costs

With effective cost management, you can secure the best stainless steel prices in a fluctuating market. When you implement a strategic approach, you can achieve cost savings to ensure you purchase the correct type of steel for your needs.
1. Buy in Bulk
One of the most effective ways to reduce costs is by ordering in bulk. Suppliers often provide volume-based discounts for larger orders, which lowers the cost per ton and can offset premiums associated with specific high-grade types.
While the initial investment may be higher, bulk purchasing can lead to long-term savings. Maintaining a steady inventory may protect you against future price hikes due to supply chain constraints or market shifts.
2. Select Appropriate Grades
Choosing the correct stainless steel grade for the intended application is another crucial way to manage costs effectively. Different grades come with varied properties, and paying extra for unnecessary features can quickly add up.
For instance, grade 304 is widely used in kitchenware and home applications due to its corrosion resistance and durability. In contrast, grade 316 offers superior resistance to chemicals and saline environments and is better suited for medical or marine uses.
By selecting grades specifically suited to the application, you can avoid overpaying for additional qualities you might not need.
3. Timing Purchases With Market Trends
Stainless steel prices can fluctuate based on demand cycles, industry trends, and global events. Monitoring these trends and timing purchases for low-demand periods can save significant costs.
For example, prices may dip during the off-season for specific industries or when supply levels are high, offering an opportunity to purchase at a discount.
Staying updated with market reports or consulting with a financial advisor familiar with metals can help you better predict ideal purchase windows.
4. Choose Reliable Suppliers
Partnering with reputable suppliers is essential in securing quality materials at competitive prices. Established suppliers with consistent quality assurance and fair pricing structures help you avoid unexpected cost fluctuations, which can be incredibly challenging in volatile markets.
Reliable suppliers also offer transparency on pricing, provide guidance on selecting the most cost-effective grades, and offer flexible payment terms or bulk discounts. Building a solid relationship with trusted suppliers can create stability and predictability in procurement costs over time.
5. Consider Long-Term Contracts or Price Hedging
For businesses needing a steady supply of stainless steel, entering into long-term contracts or hedging against price fluctuations can protect against market volatility.
Long-term contracts may allow you to lock in lower rates for an extended period while hedging—using financial strategies like futures or options—can safeguard budgets by offsetting potential price increases.
These approaches are especially beneficial in industries with predictable demand, where securing a stable cost structure supports better financial planning and pricing consistency for end products.
6. Explore Alternative Materials Where Possible
If cost management is a top priority, exploring whether alternative materials might work for specific applications is worthwhile. While stainless steel offers unique benefits, in some cases, a different material or a different stainless steel finish could be just as effective at a lower price.
For example, in non-corrosive environments, opting for a lower-grade stainless steel or even an aluminum alloy might fulfill the functional requirements at a reduced cost. Analyzing the material requirements closely with an engineer or specialist can reveal potential savings without compromising quality.
7. Invest in Efficient Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling of stainless steel can prevent costly damages and waste, helping you save over time. Implementing best practices for storage—such as using dry, well-ventilated spaces and avoiding exposure to chemicals or moisture—ensures materials maintain their integrity.
Damages incurred during transportation or due to improper storage can lead to additional expenses, either through the need for replacements or product defects. Training staff on appropriate handling techniques and investing in protective storage solutions can protect against unnecessary costs.
8. Regularly Review and Adjust Procurement Strategies
Markets are dynamic, and what worked last year may not be the best approach today.
By regularly reviewing procurement strategies and staying informed about industry developments, buyers can adjust their approach to better align with current cost trends and supply chain dynamics.
This could mean renegotiating terms with suppliers, updating inventory policies, or exploring new suppliers to stay competitive in cost management.
Conclusion: Understanding Stainless Steel Prices
The price of stainless steel is shaped by a complex interplay of market demand, geopolitical factors, and raw materials to the specific properties needed for different applications.
As most industries rely on stainless steel for its durability, corrosion resistance, and strength, understanding these price drivers is essential to making an informed purchase decision.
You can navigate the price fluctuations more effectively by considering factors like timing, grade selection, and supplier relationships.
One Response